
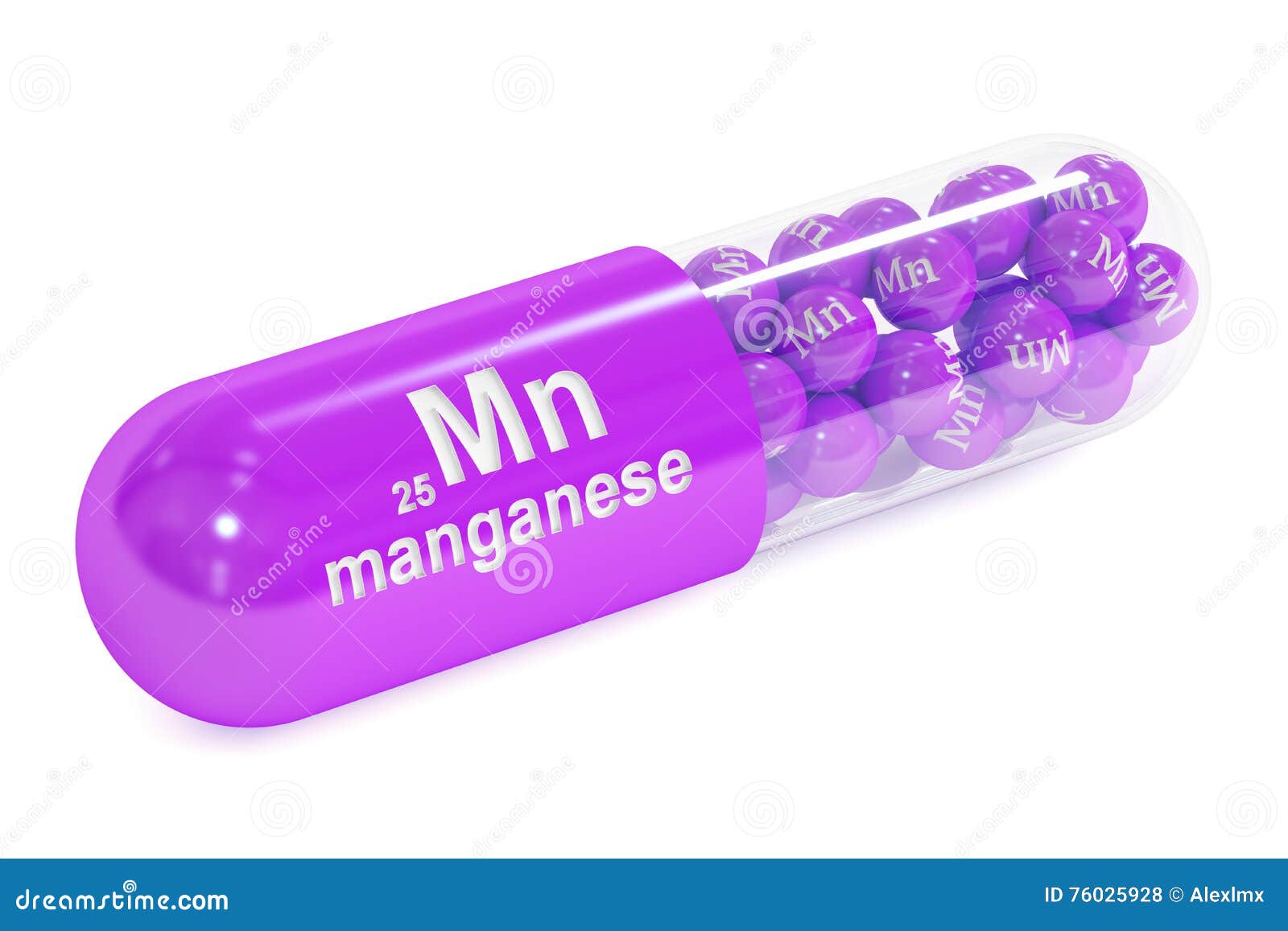
Manganese in oxidation state +7 is powerfully oxidizing, and similarly to titanium, vanadium, and chromium, it corresponds to the total number of 3d and 4s electrons. Also, the metal form of manganese is susceptible to corrosion when exposed to moist air, while it oxidizes superficially when the air is dry. The tetragonal gamma (γ) form of this chemical element forms in temperature between 1095-1135☌, while the delta (∆) form of manganese exists only above the temperature of 1134 -1245☌.īoth the chemical and physical properties of manganese resemble the respective properties of iron, except manganese metal is harder and more brittle as a substance than iron. The Beta(β) form of manganese occurs between 725 -1095☌. This complex cubic structure of Mn exists from room temperature to -725☌. Among them, the alpha phase(σ) is the most stable form of element 25. Manganese occurs in four allotropic forms. This member of the transition metals family of elements in the periodic table has an electronegativity of 1.5 according to Pauling, whereas the atomic radius according to van der Waals is 0.126 nm. It reaches its boiling point at 2061☌, 3742☏, 2334 K, while the melting point is achieved at 1246☌, 2275☏, 1519 K. With the periodic table symbol Mn, atomic number 25, atomic mass of 54.938 g.mol -1, and electron configuration 3d 5 4s 2, manganese is a very brittle and hard silvery-gray metal.
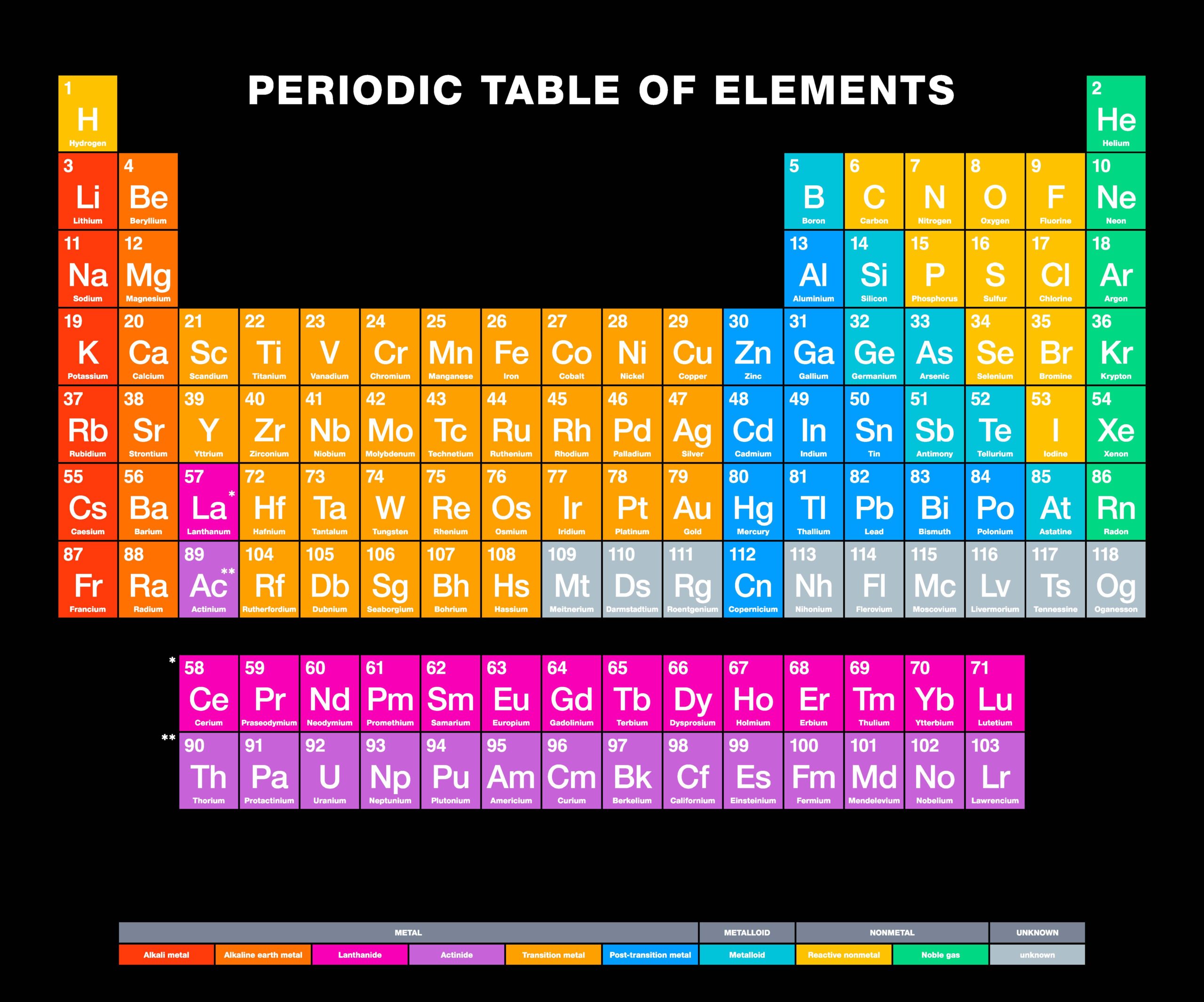
The energy of the second ionization: 1489 kJ.mol -1ĭiscovery date: In 1774 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Johan Gottlieb Gahn The energy of the first ionization: 716 kJ.mol -1 Half-life: From less than 105 nanoseconds to 3.7 million yearsĮlectronegativity according to Pauling: 1.5 Physical state: Solid at room temperature The symbol in the periodic table of elements: MnĬolor: A silvery-gray metal with a purple hue Fact Box Chemical and Physical Properties of Manganese Additionally, it plays a significant role in the development of bones and the regulation of cellular mechanisms and metabolic processes. As a trace element, this mineral also takes part in the enzyme processes in humans and animals. Manganese participates in the highly significant photosynthesis of the plants, which produces the oxygen we breathe in the atmosphere. This chemical is mostly obtained from the manganese dioxide (MnO 2 ) compound, i.e. Its most stable oxidation states are +2, +6, and +7. A member of the transition metals family of elements, manganese has four allotropic forms which make it an extremely versatile element. It’s the fifth most abundant metal that occurs in Earth’s crust. The Arabic numbering system is the most widely accepted today.Manganese is a chemical element with the atomic number 25 in the periodic table. Many periodic tables include both Roman and Arabic numbers. The modern IUPAC system uses Arabic numbers 1-18, simply numbering the columns of the periodic table from left to right.The CAS system used letters to differentiate main group (A) and transition (B) elements.The older IUPAC system used Roman numerals together with letters to distinguish between the left (A) and right (B) side of the periodic table.Three systems have been used to number families and groups: Recognizing Families on the Periodic TableĬolumns of the periodic table typically mark groups or families. Noble Gases: - Group 18 (VIIIA) - 8 valence electrons.Halogens: - Group 17 (VIIA) - 7 valence electrons.Oxygen Group or Chalcogens: - Group 16 (VIA) - 6 valence electrons.Nitrogen Group or Pnictogens: - Group 15 (VA) - 5 valence electrons.Carbon Group or Tetrels: - Group 14 (IVA) - 4 valence electrons.Boron Group or Earth Metals: Group 13 (IIIA) - 3 valence electrons.Transition Metals: Groups 3-12 - d and f block metals have 2 valence electrons.Alkaline Earth Metals: Group 2 (IIA) - 2 valence electrons.Alkali Metals: Group 1 (IA) - 1 valence electron.Many chemists and chemistry textbooks recognize five main families:Īnother common method of categorization recognizes nine element families: However, there are different ways of categorizing elements into families. Because element properties are largely determined by the behavior of valence electrons, families and groups may be the same. Element groups, on the other hand, are collections of elements categorized according to similar properties. The characteristics of the elements in these families are determined primarily by the number of electrons in the outer energy shell. Elements are classified into families because the three main categories of elements (metals, nonmetals, and semimetals) are very broad. Element families are indicated by numbers located at the top of the periodic table.Īn element family is a set of elements sharing common properties.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
